Table of Contents
ToggleEndometriosis treatment in Ayurveda works by fixing the imbalance that causes the problem. In Ayurveda, this condition is linked to aggravated Vata and Pitta dosha and improper functioning of Apana Vata. Treatment aims to reduce inflammation, regulate hormones, and clear blockages in the pelvic region. Doctors use herbal medicines, Panchakarma therapies, and diet correction. Therapies like Virechana and Basti help detoxify and improve reproductive health. Herbs support healthy menstruation and reduce tissue overgrowth. Lifestyle changes are also important. The goal is to relieve pain, improve cycle regularity, and prevent progression naturally.
What is Endometriosis?
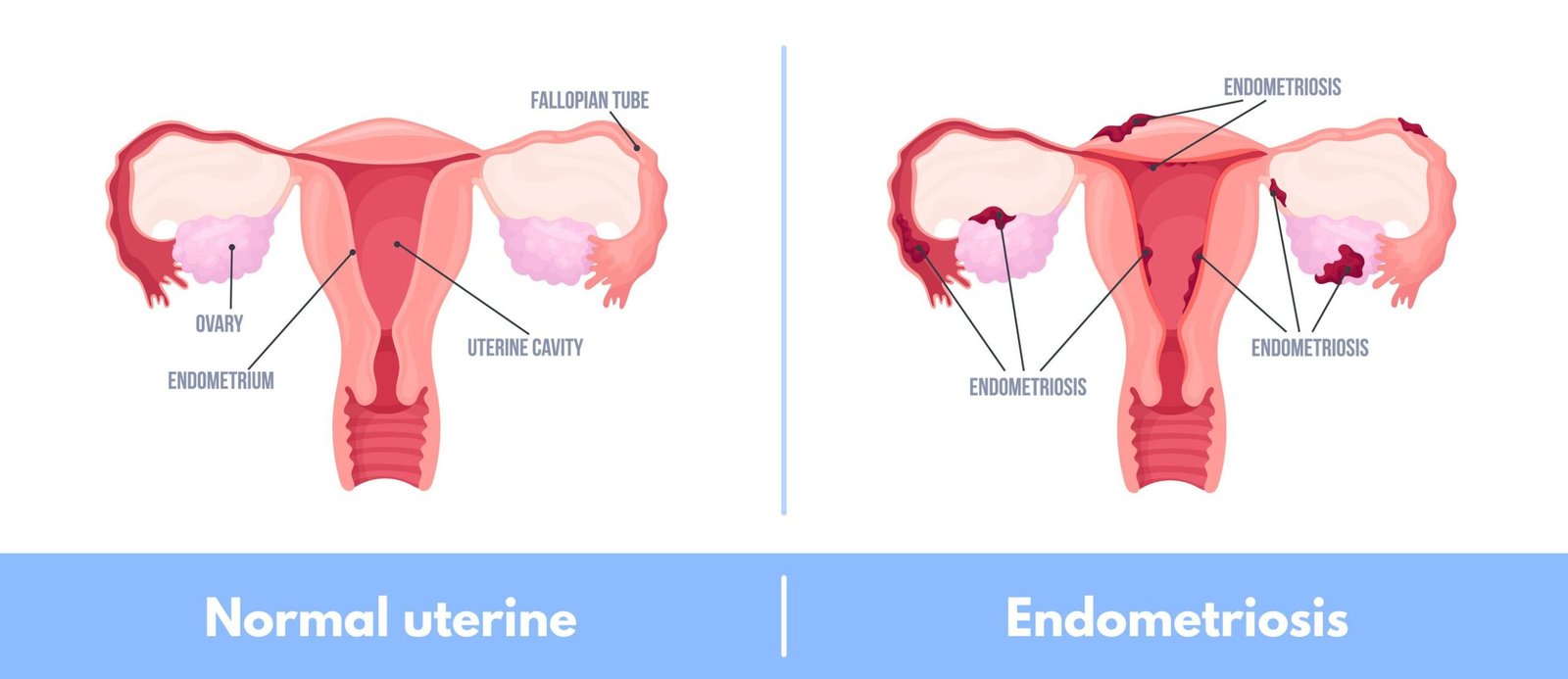
Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the inner lining of the uterus grows outside the uterus. This tissue can grow on the ovaries, pelvic lining, fallopian tubes, or nearby areas. It behaves like normal uterine lining. It thickens and bleeds during periods. But the blood cannot leave the body. This causes pain and inflammation. Many women experience severe period cramps. Some may also face fertility problems.
Endometriosis Causes
The exact cause of endometriosis is not fully known. One common reason is backward flow of menstrual blood into the pelvic area. This allows endometrial-like tissue to grow outside the uterus. Hormonal imbalance can also play a role. A weak immune system may fail to remove this tissue. Genetics may increase the risk in some women. These factors together can lead to the development of endometriosis.
How Endometriosis Develops – Modern Medical Understanding
Current research indicates a multifactorial origin:
• Retrograde menstruation allows endometrial cells into the pelvic cavity
• Estrogen dominance promotes tissue proliferation
• Immune dysfunction failing to clear ectopic cells
• Genetic predisposition
• Chronic inflammatory cytokine release
• Oxidative stress
• Environmental endocrine disruptors
These mechanisms create a sustained inflammatory pelvic environment resulting in fibrosis, adhesions, organ distortion, and pain hypersensitivity.
Clinical Symptoms
• Severe menstrual cramps resistant to painkillers
• Chronic pelvic pain between cycles
• Pain during or after intercourse
• Heavy or irregular bleeding
• Bloating, constipation, diarrhea
• Painful urination during periods
• Chronic fatigue
• Infertility
⚠️ Symptom severity does not correlate with disease stage — even minimal disease can cause severe pain.
Conditions Commonly Mistaken for Endometriosis
Endometriosis is frequently confused with:
• Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
• Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
• Uterine fibroids
• Pelvic inflammatory disease
• Urinary disorders
Proper diagnosis is essential because treatment strategies differ significantly.
Major Risk Factors & Triggers of Endometriosis
• Early onset of menstruation
• Short menstrual cycles
• Heavy bleeding
• Chronic stress & cortisol imbalance
• Hormonal disruptors (plastics, chemicals)
• Poor gut health & inflammation
• Family history
• Sedentary lifestyle
From an Ayurvedic view, long-standing Agnimandya (weak digestion), Ama accumulation, emotional stress, and improper lifestyle strongly predispose women to reproductive inflammatory disorders.
Common Sites of Endometriosis
• Ovaries (endometriomas/chocolate cysts)
• Pelvic peritoneum
• Uterosacral ligaments
• Fallopian tubes
• Rectovaginal space
• Intestines and bladder
Rarely, the disease may extend to the lungs or surgical scars.
Stages of Disease Progression
Stage 1 – Minimal: superficial inflammatory implants
Stage 2 – Mild: deeper lesions with minor scarring
Stage 3 – Moderate: ovarian cysts and adhesions
Stage 4 – Severe: extensive organ involvement and distortion
Long-Term Complications
• Chronic pelvic pain syndromes
• Impaired fertility and implantation failure
• Dense pelvic adhesions
• Digestive and urinary dysfunction
• Hormonal imbalance
• Emotional distress and reduced quality of life
Prognosis and Long-Term Outlook
With early detection and integrative management:
✔ Pain can significantly reduce
✔ Disease progression can slow
✔ Fertility outcomes improve
✔ Quality of life is restored
Without treatment, inflammation and fibrosis typically worsen over time.
Endometriosis behaves as a chronic inflammatory condition requiring sustained systemic management — similar to arthritis or autoimmune disorders.
Classical Ayurvedic Correlation
Charaka Samhita describes:
“Vitiated Apana Vata obstructed by Kapha and inflamed by Pitta produces painful pelvic disorders and abnormal growths.”
Sushruta explains that chronic Rakta Dushti leads to:
Granthi formation with inflammation and tissue hardness.
Ashtanga Hridaya further links Ama with cystic and fibrotic disorders.
These collectively align with modern endometriosis pathology.
Prevalence and Diagnostic Challenges
Endometriosis affects approximately 1 in 10 women of reproductive age worldwide. However, diagnosis is commonly delayed by 7–10 years due to:
• Normalization of painful periods
• Misdiagnosis as IBS, PCOS, fibroids, or urinary disorders
• Limited early detection through routine imaging
• Lack of awareness of chronic inflammatory gynecological disorders
Delayed diagnosis allows disease progression, increasing chronic pain, adhesion formation, hormonal dysfunction, and fertility complications.
Modern Diagnostic Evaluation of Endometriosis
Diagnosis is based on a combination of:
Clinical Assessment
• Detailed menstrual pain history
• Pelvic pain mapping
• Fertility evaluation
Imaging
• Transvaginal ultrasound for ovarian cysts
• MRI for deep infiltrating disease
Gold Standard
✔ Diagnostic laparoscopy with biopsy confirmation
Ayurveda additionally evaluates:
• Agni (digestive strength)
• Ama’s presence
• Dosha imbalance
• Menstrual quality (Artava Pariksha)
This combined assessment allows early detection and individualized therapy.
Neuro-Inflammatory Pain Mechanism in Endometriosis
Recent research shows that endometriosis is not only a hormonal disease but also a chronic pain sensitization disorder.
Ectopic implants release:
• Pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, prostaglandins)
• Nerve growth factors that increase pain fiber density
• Oxidative stress molecules damaging pelvic tissues
This leads to:
✔ Hyper-sensitive pelvic nerves
✔ Pain amplification even with minimal lesions
✔ Chronic pain memory in the nervous system
This explains why pain may persist even after surgery — emphasizing the need for systemic inflammatory control rather than only lesion removal.
Ayurvedic Interpretation of Endometriosis
Though not named directly in classical texts, endometriosis closely corresponds with:
• Yonivyapad (gynecological disorders – Charaka Samhita)
• Artava Dushti (menstrual pathology – Sushruta Samhita)
• Granthi & Arbuda (cystic/proliferative growths – Ashtanga Hridaya)
• Rakta Pradoshaja Vikara (blood inflammatory disorders)
Core Dosha Imbalances
Apana Vata Disturbance – Charaka Samhita
→ Pelvic pain, stagnation, abnormal tissue movement, irregular menstruation
Pitta Aggravation – Sushruta Samhita
→ Inflammation, burning pain, heavy bleeding, tissue irritation
Kapha Accumulation – Ashtanga Hridaya
→ Cyst formation, fibrosis, thick adhesions
Ama Accumulation
→ Chronic inflammation, hormonal resistance, and immune dysfunction
Ayurvedic Samprapti (Disease Pathogenesis)
Weak digestion → Ama formation
↓
Vata dysregulation → pelvic stagnation
↓
Pitta-driven inflammation
↓
Kapha tissue overgrowth
↓
Rakta & Mamsa involvement → ectopic inflammatory implants
Ayurvedic Treatment for Endometriosis
In Ayurveda, Panchakarma Therapies are used to treat Endometriosis. These therapies or treatments help remove toxins and calm the dosha imbalance linked to pain and inflammation. They also support healthy hormone function and improve pelvic health.
✔ Virechana Therapy for Endometriosis Treatment
• Clears inflammatory Pitta
• Detoxifies liver & hormonal metabolism
• Reduces pelvic congestion
Learn more about- Virechana Therapy
✔ Medicated Basti Therapy (Primary Vata treatment – Charaka) for Endometriosis
• Relieves chronic pelvic pain
• Improves pelvic circulation
• Reduces adhesions
Learn more about- Medicated Basti Therapy
✔ Uttar Basti for Endometriosis Treatment
• Local uterine healing
• Enhances tissue repair
• Regulates cycles
Learn more about- Uttar Basti
Ayurvedic Remedies for Endometriosis
Ayurvedic remedies for endometriosis focus on supporting hormone balance and reducing inflammation naturally. These herbs help improve uterine health and ease pain. They also help clear toxins and support healthy blood flow. Some herbs help in reducing Endometriosis cysts and swelling. Others calm the body and reduce stress. Together, these remedies help improve menstrual health and overall reproductive wellbeing.
- Shatavari – hormonal modulation
- Ashoka – uterine health
- Kanchanar Guggulu – cyst resolution
- Manjistha – anti-inflammatory blood purifier
- Dashamoola – pain & swelling control
- Triphala – detoxification
- Ashwagandha – stress & cortisol balance
Ayurvedic Diet for Endometriosis
An Ayurvedic diet for endometriosis focuses on reducing inflammation and balancing hormones. This diet helps improve digestion, reduce pain, and support healthy menstrual cycles.
Diet to Eat in Endometriosis Ayurvedic Treatment
• Warm, fresh foods
• Anti-inflammatory spices
• Light, digestible meals
• Adequate hydration
• Healthy fats
Diet to Avoid during Endometriosis
• Processed foods
• Refined sugar
• Cold beverages
• Fried food
• Caffeine
• Chemicals & preservatives
Lifestyle Interventions for Endometriosis
• Daily Abhyanga massage
• Gentle yoga & pelvic relaxation
• Pranayama breathing
• Restful sleep cycles
Stress management is essential for hormonal regulation.
Preventive & Disease Control Strategies
While endometriosis cannot always be fully prevented, progression can be minimized through:
• Early pain evaluation
• Anti-inflammatory nutrition
• Hormonal balance
• Gut health improvement
• Stress reduction
• Regular menstrual health monitoring
Ayurveda emphasizes Nidana Parivarjana — removing disease triggers as the first step of healing.
Fertility Support
By improving pelvic inflammation, ovarian micro-environment, hormonal signaling, and implantation physiology, integrative Ayurvedic therapy often enhances natural conception and IVF success rates.
When Conventional Treatment Is Necessary
Immediate medical care is essential for:
• Large cyst rupture risk
• Severe organ involvement
• Dense adhesions
• Uncontrolled bleeding
• Acute complications
Integrative care complements — not replaces — emergency treatment.
Endometriosis Care at Adyant Ayurveda – Bangalore
Physician-supervised programs include:
• Panchakarma detox protocols
• Individualized herbal therapy
• Nutrition & lifestyle counselling
• Fertility-supportive treatment
Call to book an appointment at 9972541009
FAQs on Ayurvedic Treatment for Endometriosis
What exactly causes endometriosis to keep progressing?
Chronic inflammation, estrogen dominance, immune dysfunction, oxidative stress, and fibrosis create a self-sustaining disease loop unless corrected systemically.
Is endometriosis curable permanently?
There is no single permanent cure, but integrative management can place the disease into long-term remission with major symptom relief.
Can young girls develop endometriosis?
Yes — it can begin soon after the first menstruation.
Does pregnancy cure endometriosis?
Pregnancy may temporarily suppress symptoms, but it does not cure the disease.
Is a hysterectomy a solution?
Not always. Endometriosis exists outside the uterus, so symptoms may persist.
Can Ayurvedic therapy shrink cysts?
Many patients show cyst reduction and inflammation control with proper protocols.
How long should treatment continue?
Typically, 3–12 months, depending on severity and response.
Can stress worsen symptoms?
Yes. Stress hormones directly increase inflammation and pain sensitivity.
Is hormonal medication harmful long-term?
Long-term use may have side effects and does not address the root inflammation.
When should I seek urgent care?
• Sudden severe pain
• Heavy bleeding
• Fever
• Bowel or urinary obstruction symptoms
Research-Based References on Endometriosis
Oxidative stress & disease progression (PubMed)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40052588/Inflammation and fertility impact (PubMed)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39229427/Oxidative stress severity correlation (PubMed)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31007466/Systematic review on oxidative stress (PubMed)
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29057034/Endometrioma & infertility oxidative damage (Nature Scientific Reports)
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-20319-9Ayurvedic perspective & clinical relevance
https://jaims.in/jaims/article/view/219Documented Ayurvedic management case study
https://ijapr.in/index.php/ijapr/article/view/3805
Educational Disclaimer: This article is for educational purposes only and does not replace medical advice. Treatment results may vary. Please consult a qualified Ayurvedic doctor or healthcare professional before starting any treatment.
Last Updated: 16 February 2026
Content Update Policy
Our articles are reviewed and refreshed regularly to reflect the latest information. Our experts continuously monitor developments in the health and wellness field to ensure the content remains accurate and up to date.
Author: Dr. Shree Lakshmi, BAMS
Senior Ayurvedic Physician, Adyant Ayurveda
Medical Reviewer: Dr. Sumana Patvardhan, MD (Ayurveda)
Consultant Ayurvedic Physician, Adyant Ayurveda