Table of Contents
ToggleMedically reviewed Ayurvedic content | Doctor-guided, evidence-aligned approach
Introduction: Why Your Belly Doesn’t Reduce Despite Diet & Exercise
Many individuals struggle with a stubborn, protruding abdomen even after following calorie-restricted diets, gym routines, or intermittent fasting. This condition is commonly referred to as ‘pot belly syndrome’.
Unlike general obesity, pot belly syndrome is often a sign of digestive dysfunction, gut imbalance, toxin accumulation (Ama), and impaired liver detoxification, rather than excess body fat alone. This explains why conventional weight-loss strategies frequently fail to produce lasting results.
Ayurvedic treatment for pot belly syndrome focuses on correcting digestion, healing the gut, and restoring liver function — the real drivers behind abdominal distension.
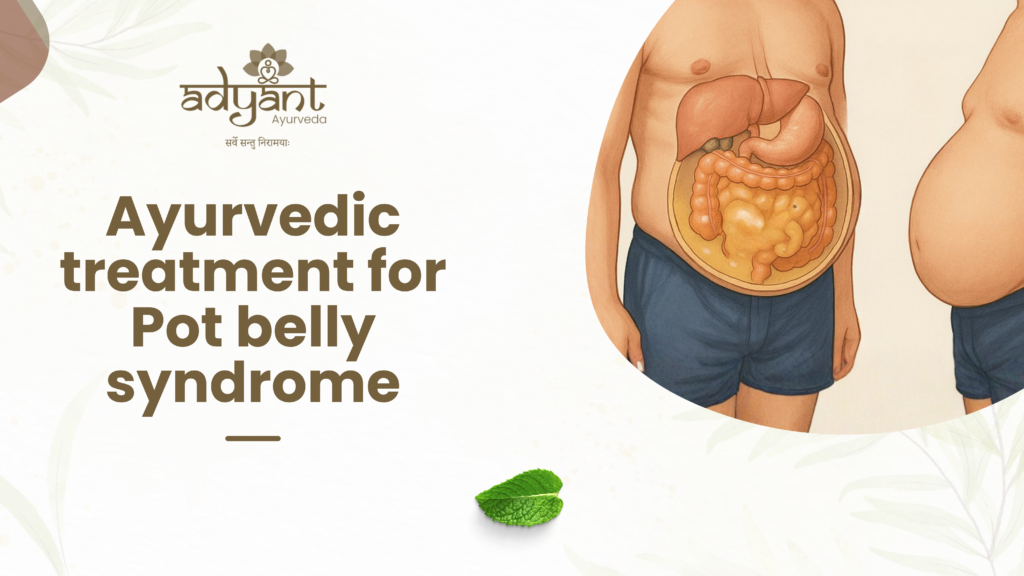
What Is Pot Belly Syndrome?
Pot Belly Syndrome is a functional digestive–metabolic condition characterized by a hard, protruding abdomen, often accompanied by bloating and digestive discomfort.
It is not a standalone disease but a cluster of underlying issues involving:
- Weak digestive fire (Mand Agni)
- Gut microbial imbalance (similar to SIBO)
- Liver overload and fatty changes
- Chronic toxin accumulation (Ama)
Pot Belly vs Abdominal Fat: Key Differences
| Feature | Pot Belly Syndrome | Abdominal Fat |
|---|---|---|
| Texture | Hard, tight | Soft, pinchable |
| Timing | Worse by evening | Constant |
| Weight | Often normal | Usually increased |
| Digestion | Poor, bloating | Often normal |
| Exercise response | Minimal | Improves with fat loss |
This distinction is essential for choosing the right Ayurvedic treatment plan.
Root Causes of Pot Belly Syndrome (Modern & Ayurvedic View)
1. Weak Digestion (Mand Agni)
According to Ayurveda, Agni (digestive fire) governs digestion, absorption, and metabolism. When Agni becomes weak:
- Food is not digested properly
- Fermentation and gas increase
- Nutrient absorption reduces
- Metabolic waste accumulates
This leads directly to bloating, heaviness, and abdominal distension.
2. Leaky Gut & SIBO-Like Gut Imbalance
Poor digestion creates an environment conducive to bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine, similar to SIBO (Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth).
This causes:
- Excess gas production
- Abdominal pressure
- Inflammation of the gut lining
- Increased intestinal permeability (leaky gut)
Ayurvedic treatment for pot belly syndrome addresses this through digestive correction, gut-healing herbs, and antimicrobial support, not symptom suppression.
3. Fatty Liver & Impaired Detoxification
The liver plays a central role in:
- Fat metabolism
- Toxin elimination
- Hormonal regulation
- Bile secretion for digestion
When overloaded by processed foods, alcohol, stress, or metabolic dysfunction, the liver becomes sluggish, contributing to:
- Fatty liver changes
- Poor fat breakdown
- Increased abdominal congestion
This explains the strong gut–liver connection in pot belly syndrome.
Read our blog on Ayurvedic Treatment for Fatty Liver to learn about its treatment, causes, symptoms, Panchakarma treatments, herbs, and diet.
4. Ama (Toxin) Accumulation – Ayurvedic Explanation
Ama refers to undigested metabolic waste that blocks bodily channels (srotas). When Ama accumulates:
- Inflammation increases
- Metabolism slows
- Fat and fluids stagnate in the abdomen
Ayurvedic detoxification focuses on removing Ama safely, not extreme fasting or crash detoxes.
Common Signs & Symptoms You Should Not Ignore
Pot belly syndrome is often accompanied by:
- Persistent bloating and gas
- Hard, protruding abdomen
- Acidity or reflux
- Constipation or loose stools
- Fatigue after meals
- Reduced appetite or cravings
- White tongue coating
These symptoms indicate digestive and metabolic imbalance, not cosmetic fat.
What Happens If Pot Belly Syndrome Is Left Untreated?
Ignoring pot belly syndrome may lead to:
- Progression of fatty liver disease
- Insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome
- Hormonal imbalances
- Chronic gut inflammation
- Nutrient deficiencies
This article is informational and not a substitute for a medical diagnosis.
How Pot Belly Syndrome Is Diagnosed
A proper diagnosis involves:
- Detailed digestive and dietary history
- Abdominal examination
- Assessment of bowel patterns
- Liver health indicators
- Metabolic risk evaluation
At Adyant Ayurveda, diagnosis focuses on identifying Agni strength, Ama presence, dosha imbalance, and gut–liver dysfunction, ensuring personalized care.
Ayurvedic Understanding of Pot Belly Syndrome
From an Ayurvedic perspective:
- Kapha causes heaviness and stagnation
- Pitta imbalance affects the liver and bile
- Weak Agni initiates toxin formation
Spot fat reduction does not work because the issue lies in systemic metabolism, not localized fat storage.
Ayurvedic Treatment for Pot Belly Syndrome
1. Gut Healing & Digestive Correction
- Strengthening Agni
- Reducing fermentation and gas
- Supporting gut lining integrity
2. Liver Detoxification & Metabolic Support
- Improving bile flow
- Enhancing fat metabolism
- Supporting natural detox pathways
3. Ama Reduction & Metabolic Reset
- Gentle internal cleansing
- Removing metabolic toxins
- Restoring cellular function
4. Personalized Diet & Lifestyle Protocol
- Warm, cooked, easy-to-digest meals
- Avoidance of cold, processed foods
- Correct meal timing
- Stress and sleep regulation
Treatments are doctor-supervised and individualized.
How Long Does It Take to See Results?
- 2–3 weeks: Reduced bloating, improved digestion
- 4–6 weeks: Visible reduction in abdominal distension
- 8–12 weeks: Improved liver and metabolic health
Timelines vary based on severity and compliance.
Why Adyant Ayurveda’s Approach Is Different
- Root-cause diagnosis, not symptom masking
- Experienced Ayurvedic doctors
- Integration of classical Ayurveda with modern understanding
- Personalized, non-generic treatment protocols
- Focus on gut health, liver health, and sustainable recovery
When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Consult a doctor urgently if you experience:
- Severe abdominal pain
- Rapid abdominal swelling
- Jaundice
- Persistent vomiting
- Unexplained weight loss
Conclusion: Flat Belly Starts With a Healthy Gut & Liver
Pot belly syndrome is a signal, not a flaw. It indicates that digestion, gut balance, and liver detoxification need attention. Ayurvedic treatment for pot belly syndrome offers a safe, sustainable, and root-cause-based approach to restore metabolic health and naturally reduce abdominal distension.
Trusted Care at Adyant Ayurveda
At Adyant Ayurveda, treatment for pot belly syndrome is doctor-guided, personalized, and evidence-aligned, focusing on gut healing, liver detoxification, and metabolic balance.
Consult our Ayurvedic doctors for a detailed assessment and customized plan.
FAQs on Ayurvedic Treatment for Pot Belly Syndrome
What exactly is Pot Belly Syndrome?
Pot Belly Syndrome is a condition where the abdomen appears hard, protruded, and bloated despite normal body weight or regular exercise. It is usually caused by poor digestion, gut imbalance, toxin accumulation (Ama), and liver dysfunction, rather than excess fat.
Is pot belly the same as abdominal fat?
No. Pot belly is different from abdominal fat. Pot belly feels hard and tight, worsens after meals or by evening, and does not reduce easily with exercise. Abdominal fat is usually soft and responds to calorie control and workouts.
Can poor digestion really cause pot belly?
Yes. According to Ayurveda, weak digestive fire (Mand Agni) leads to incomplete digestion, gas formation, and toxin buildup. This causes bloating, abdominal pressure, and metabolic slowdown, resulting in a persistent pot belly.
Is there a connection between pot belly and fatty liver?
Yes. The gut–liver connection is strong. When digestion is weak and toxins accumulate, the liver becomes overloaded, affecting fat metabolism and bile secretion. This can contribute to fatty liver and abdominal distension.
Does Ayurveda consider pot belly a disease?
Ayurveda does not classify pot belly as a single disease. It is considered a functional imbalance involving Agni (digestion), Ama (toxins), and Kapha–Pitta doshas, affecting the gut, liver, and metabolism.
Can Ayurveda help reduce pot belly naturally?
Yes. Ayurveda focuses on root-cause treatment, including:
- Improving digestion (Agni deepana)
- Gut healing and microbiome balance
- Liver detoxification
- Ama elimination
- Personalized diet and lifestyle correction
This approach supports natural and sustainable reduction of pot belly.
How long does Ayurvedic treatment take to show results?
Most individuals notice:
- Reduced bloating and gas within 2–3 weeks
- Visible abdominal reduction in 4–6 weeks
- Improved gut and liver health in 8–12 weeks
Results vary depending on severity, lifestyle, and adherence.
Is Panchakarma required for pot belly treatment?
Not always. Mild to moderate cases may improve with herbs, diet, and lifestyle changes.
Panchakarma therapies like Virechana or Basti may be recommended in chronic or toxin-heavy cases, always under doctor supervision.
Can SIBO or leaky gut cause pot belly?
Yes. Conditions similar to SIBO and leaky gut cause excessive gas, bloating, and inflammation. Ayurveda addresses these by correcting digestion, reducing fermentation, and restoring gut integrity instead of only suppressing symptoms.
What foods should be avoided if I have pot belly syndrome?
Commonly avoided foods include:
- Cold and refrigerated foods
- Fried and oily items
- Excess sugar and refined carbs
- Carbonated drinks
- Late-night heavy meals
These weaken digestion and worsen toxin buildup.
Is a pot belly dangerous if left untreated?
If ignored, pot belly syndrome may progress to:
- Fatty liver disease
- Insulin resistance
- Hormonal imbalance
- Chronic digestive disorders
Early diagnosis and treatment help prevent long-term metabolic complications.
Can exercise alone fix pot belly syndrome?
Exercise alone is usually not sufficient. Without correcting digestion, gut health, and liver function, exercise may not reduce pot belly effectively. Ayurveda emphasizes internal correction first, then physical activity.
Who should seek medical evaluation for a pot belly?
You should consult a doctor if a pot belly is associated with:
- Persistent pain
- Rapid abdominal enlargement
- Jaundice
- Vomiting
- Sudden weight loss
This ensures serious conditions are ruled out.
How does Adyant Ayurveda approach pot belly syndrome?
At Adyant Ayurveda, treatment is:
- Doctor-supervised
- Root-cause focused
- Personalized to digestion, gut, and liver health
- Based on classical Ayurveda and modern assessment
The goal is sustainable metabolic healing, not temporary belly reduction.
Note: Ayurvedic treatment should always be undertaken under the supervision of a qualified Ayurvedic physician. Individual results may vary based on diagnosis, constitution, and compliance.
Treatment protocols described are based on the clinical experience and Ayurvedic assessment framework followed by Dr. Shree Lakshmi at Adyant Ayurveda.
Medically Reviewed By
Dr. Shree Lakshmi, BAMS, MD (Ayurveda)
Senior Ayurvedic Physician – Gut, Liver & Metabolic Disorders
Clinical Experience: 28 years of experience in Ayurveda and PanchakarmaThis content has been medically reviewed by Dr. Shree Lakshmi for clinical accuracy, patient safety, and alignment with classical Ayurvedic texts and modern digestive–metabolic understanding.