Table of Contents
ToggleAyurvedic treatment for fatty liver focuses on healing the liver from the root. It does not just aim to reduce liver enzyme levels. It works to improve digestion and metabolism. It helps remove toxin buildup from the body. It supports the liver in clearing excess fat naturally.
With the help of herbs, simple detox therapies, diet correction, and daily routine changes, the goal is to restore healthy liver function step by step and prevent further damage in a natural way.
At Adyant Ayurveda, we’ve successfully reversed fatty liver in many patients using Panchakarma, herbal medicines, dietary therapy, and personalized lifestyle correction, deeply rooted in Ayurvedic principles.
📌 Case Insight: A 38-year-old male with NAFLD and borderline diabetes underwent Virechana and 45 days of herbal therapy at Adyant Ayurveda. The result? Marked improvement in liver enzyme levels, reduction in bloating, and a healthy weight loss of 6 kg.
What is Fatty Liver?
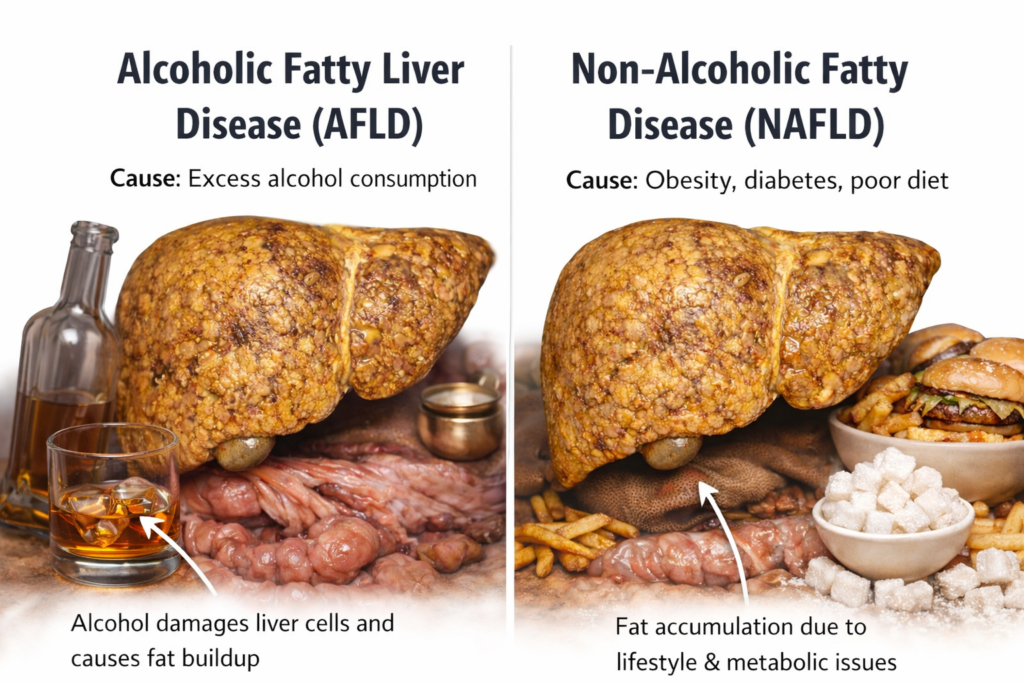
Fatty liver occurs when excess fat builds up in liver cells. If unmanaged, it can lead to Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH), fibrosis, cirrhosis, and even liver failure. Types include:
Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (AFLD)
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Ayurvedic Pathology (How and Why a Fatty liver develops)
In Ayurveda, fatty liver correlates with Yakrit Roga and is often rooted in:
Medo Dhatu Vriddhi – an increase in fat tissue (medas)
Srotorodha – blockage of bodily channels
Ama Accumulation – due to poor digestion and metabolism
🧠 From an Ayurvedic viewpoint, the progression from mild fatty liver to cirrhosis reflects deepening doshic imbalance, with aggravated Ama affecting Rakta Dhatu (blood tissue) and Yakrit (liver).
What is the difference between a fatty liver and a normal liver?
Your liver is like the body’s cleaning department. It digests food, removes toxins, manages fat, and keeps your blood clean. When the liver is healthy, everything runs smoothly. When it’s overloaded, problems start.
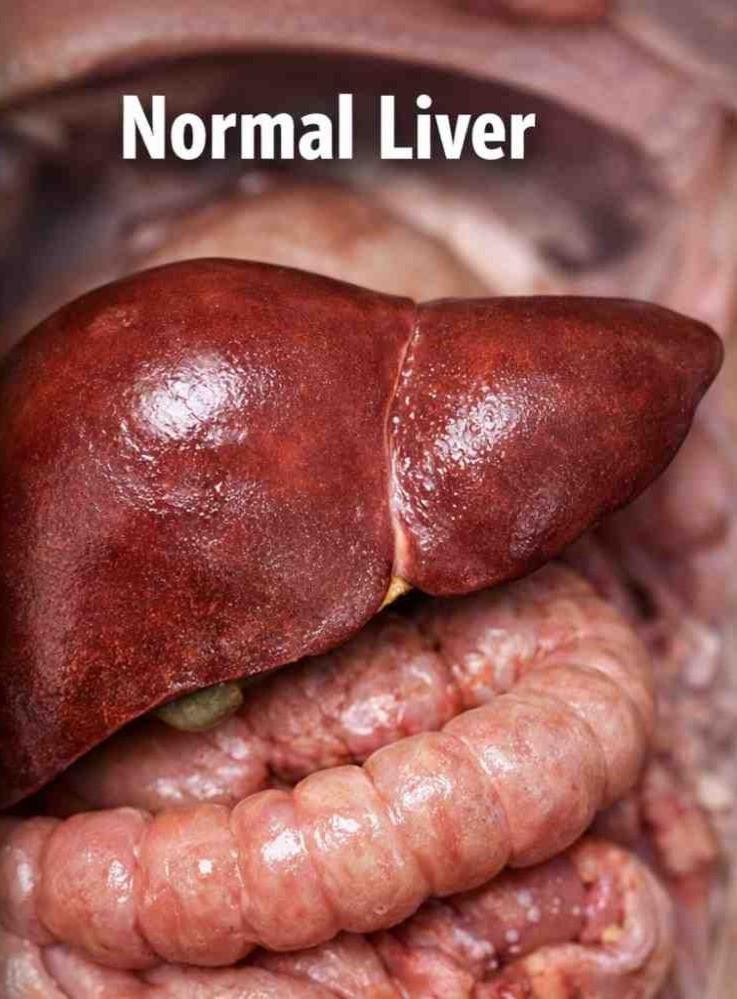
What is a Normal Liver?
A normal liver is balanced and strong.
- It is smooth, firm, and reddish-brown in color
- Fat inside the liver is very minimal
- Digestion works well
- Energy levels are good
- Toxins are properly removed
From an Ayurvedic view, n0rmal liver means:
- Agni (digestive fire) is strong
- Pitta dosha is balanced
- No excess Ama (toxins)
- Blood is clean and nourishing the body
Such a liver keeps your skin clear, weight controlled, and mind sharp.
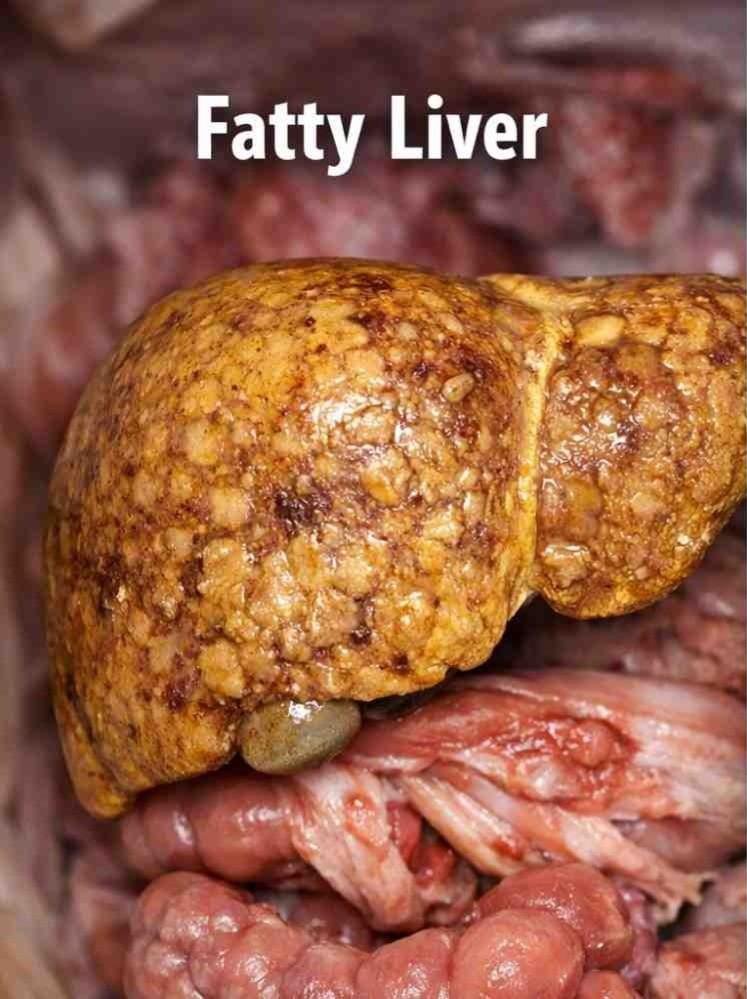
What is a Fatty Liver?
A fatty liver means fat has started collecting inside liver cells.
- Liver becomes enlarged and yellowish
- Fat covers liver tissues like grease on a filter
- Liver functions slow down
- Person feels tired, heavy, or bloated
- Often linked with weight gain and poor digestion
From an Ayurvedic view, Fatty liver happens due to:
- Weak Agni
- Excess Kapha dosha
- Accumulation of Ama (undigested toxins)
- Overuse of oily, fried, sweet, and processed foods
- Lack of physical activity
In Ayurveda, fatty liver is mainly a Kapha-Pitta disorder.
Symptoms of Fatty Liver
- Persistent fatigue
- Mild pain in the right upper abdomen
- Abdominal bloating or fullness
- Loss of appetite
- Brain fog
- Jaundice (advanced stages)
- Elevated liver enzymes (detected in blood tests)
Causes of Fatty Liver
- Excess alcohol intake (AFLD)
- Obesity, poor diet, and sedentary habits
- High cholesterol or triglycerides
- Diabetes or insulin resistance
- PCOD or hormonal imbalances
- Rapid weight loss or crash dieting
- Prolonged use of medications (steroids, tamoxifen)
Ayurvedic Understanding of Fatty Liver
Ayurveda doesn’t just view fatty liver as a physical disorder—it understands it as a result of dosha imbalance and metabolic toxicity.
Key Pathological Factors:
- Pitta aggravation: Causes inflammation and liver tissue irritation
- Kapha accumulation: Leads to fat deposition and sluggish digestion
- Ama build-up: Undigested metabolic waste obstructing channels (Srotas)
🔍 “In Ayurvedic pathology, fatty liver is often linked to Medo Dhatu Vriddhi, leading to Srotorodha and liver dysfunction due to accumulated Ama.”
Healing Goals in Ayurveda:
- Strengthen Agni (digestive fire)
- Detoxify Ama and cleanse channels
- Balance Pitta and Kapha doshas
- Rejuvenate Yakrit (liver) function
Panchakarma for Liver Detox
Panchakarma therapy is the most powerful Ayurvedic tool for internal purification and metabolic reset.
Recommended Panchakarma Therapies for Fatty Liver:
- Virechana (Purgation): Eliminates toxins from the liver-bowel axis and reduces Pitta-Kapha
- Basti (Medicated Enema): Cleanses the colon and balances metabolism
- Abhyanga & Swedana: Boosts lymphatic drainage and reduces Ama
- Shirodhara: Reduces stress, which impacts metabolic balance
🧪 “At Adyant Ayurveda, Virechana has shown remarkable improvement in patients with NAFLD by lowering liver enzyme levels and reducing fatty infiltration.”
Best Ayurvedic Herbs for Fatty Liver
| Herb | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Phyllanthus niruri (Bhumi Amla) | Strong hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity – effective in NAFLD |
| Kutki (Picrorhiza kurroa) | Stimulates bile flow, detoxifies the liver, anti-inflammatory |
| Kalmegh (Andrographis) | Powerful Pitta-shamaka, liver stimulant, reduces inflammation |
| Punarnava | Diuretic and anti-inflammatory, supports the liver and kidneys |
| Triphala | Gentle detox improves digestion and metabolism |
🧬 “Studies have shown that Phyllanthus niruri exhibits strong hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects, beneficial in managing NAFLD.”
Top Ayurvedic Medicines for Fatty Liver
Here are classical Ayurvedic formulations that may be prescribed under supervision:
- Arogyavardhini Vati – Liver detox, balances all three doshas
- Punarnavadi Mandura – Reduces fluid retention, improves blood profile
- Phalatrikadi Kwatha – Liver stimulant, reduces inflammation
- Avipattikar Churna – Balances Pitta, supports liver-gut detox
- Liv 52 / Livomap – Herbal formulations for hepatoprotection
✅ Always consult an Ayurvedic physician before starting herbal medicines. Self-medication is discouraged.
Diet Recommendations for Fatty Liver in Ayurveda
🍽️ What to Eat:
- Light, warm meals like khichdi, steamed veggies, soups
- Spices like turmeric, ginger, jeera, and ajwain
- Fruits like apple, papaya, pomegranate, and amla
- Bitter greens: methi, karela, neem
❌ What to Avoid:
- Fried, spicy, fermented, or packaged food
- Sugary beverages and white sugar
- Dairy-heavy meals and red meat
- Alcohol, carbonated drinks, and caffeine
Lifestyle Modifications
- Practice daily yoga and morning walks
- Integrate Pranayama and meditation
- Eat early dinners and avoid daytime sleeping
- Avoid alcohol and smoking
- Ensure adequate hydration
Home Remedies for Fatty Liver
These simple remedies can complement Ayurvedic treatment:
- Warm water with lemon every morning
- Amla juice (10 ml) on empty stomach
- 1 tsp turmeric + ½ tsp ginger powder in warm water before bed
- Triphala churna at night to improve digestion
- Fenugreek seed water soaked overnight and consumed in the morning
Read our blog on Ayurvedic Treatment for Pot Belly Syndrome and improve your Gut, Liver & metabolic health.
How Adyant Ayurveda Can Help
At Adyant Ayurveda, we combine authentic classical protocols with modern diagnostics to offer tailored treatment for fatty liver.
Why Choose Us?
- 24+ years of expertise in Panchakarma & liver disorders
- Personalized treatment plans with qualified Ayurvedic doctors
- 4 centers across Bangalore: Jayanagar, Indiranagar, Kalyan Nagar, RR Nagar
- Specialized therapies like Virechana, Basti, herbal lepas, and diet counseling
- Proven success stories and patient outcomes
📞 Call 9972541009 to book a consultation and get started with your healing journey.
FAQs on Ayurvedic Treatment for Fatty Liver
Can Ayurveda cure fatty liver completely?
With early intervention, Ayurveda can reverse fatty liver by addressing root causes, detoxifying the liver, and balancing metabolism.
Is Panchakarma necessary?
Panchakarma like Virechana is highly recommended for moderate to severe NAFLD cases. It enhances liver function and cleanses accumulated Ama.
How long does Ayurvedic treatment take?
Typically 30–90 days depending on severity and patient compliance.
Can I follow Ayurvedic treatment alongside allopathic medicines?
Yes, under supervision. Our doctors will guide integrated protocols if needed.
Conclusion
Fatty liver is more than just fat accumulation—it’s a metabolic disorder rooted in doshic imbalance and poor digestion. Ayurveda views it holistically and offers natural, lasting solutions through diet, detox, herbs, and lifestyle correction.
If you’re looking for safe, side-effect-free, and sustainable recovery, consult with our experienced team at Adyant Ayurveda.
🌿 Your liver deserves better. Let Ayurveda heal from within.









